Class JTextComponent
- All Implemented Interfaces:
ImageObserver, MenuContainer, Serializable, Accessible, Scrollable
- Direct Known Subclasses:
JEditorPane, JTextArea, JTextField
JTextComponent is the base class for swing text
components. It tries to be compatible with the
java.awt.TextComponent class
where it can reasonably do so. Also provided are other services
for additional flexibility (beyond the pluggable UI and bean
support).
You can find information on how to use the functionality
this class provides in
General Rules for Using Text Components,
a section in The Java Tutorial.
- Caret Changes
-
The caret is a pluggable object in swing text components.
Notification of changes to the caret position and the selection
are sent to implementations of the
CaretListenerinterface that have been registered with the text component. The UI will install a default caret unless a customized caret has been set.
By default the caret tracks all the document changes performed on the Event Dispatching Thread and updates it's position accordingly if an insertion occurs before or at the caret position or a removal occurs before the caret position.DefaultCarettries to make itself visible which may lead to scrolling of a text component withinJScrollPane. The default caret behavior can be changed by theDefaultCaret.setUpdatePolicy(int)method.
Note: Non-editable text components also have a caret though it may not be painted. - Commands
-
Text components provide a number of commands that can be used
to manipulate the component. This is essentially the way that
the component expresses its capabilities. These are expressed
in terms of the swing
Actioninterface, using theTextActionimplementation. The set of commands supported by the text component can be found with thegetActions()method. These actions can be bound to key events, fired from buttons, etc. - Text Input
-
The text components support flexible and internationalized text input, using
keymaps and the input method framework, while maintaining compatibility with
the AWT listener model.
A
Keymaplets an application bind key strokes to actions. In order to allow keymaps to be shared across multiple text components, they can use actions that extendTextAction.TextActioncan determine whichJTextComponentmost recently has or had focus and therefore is the subject of the action (In the case that theActionEventsent to the action doesn't contain the target text component as its source).The Input Method Framework lets text components interact with input methods, separate software components that preprocess events to let users enter thousands of different characters using keyboards with far fewer keys.
JTextComponentis an active client of the framework, so it implements the preferred user interface for interacting with input methods. As a consequence, some key events do not reach the text component because they are handled by an input method, and some text input reaches the text component as committed text within anInputMethodEventinstead of as a key event. The complete text input is the combination of the characters inkeyTypedkey events and committed text in input method events.The AWT listener model lets applications attach event listeners to components in order to bind events to actions. Swing encourages the use of keymaps instead of listeners, but maintains compatibility with listeners by giving the listeners a chance to steal an event by consuming it.
Keyboard event and input method events are handled in the following stages, with each stage capable of consuming the event:
Stages of keyboard and input method event handling Stage KeyEvent InputMethodEvent 1. input methods (generated here) 2. focus manager 3. registered key listeners registered input method listeners 4. input method handling in JTextComponent 5. keymap handling using the current keymap 6. keyboard handling in JComponent (e.g. accelerators, component navigation, etc.) To maintain compatibility with applications that listen to key events but are not aware of input method events, the input method handling in stage 4 provides a compatibility mode for components that do not process input method events. For these components, the committed text is converted to keyTyped key events and processed in the key event pipeline starting at stage 3 instead of in the input method event pipeline.
By default the component will create a keymap (named DEFAULT_KEYMAP) that is shared by all JTextComponent instances as the default keymap. Typically a look-and-feel implementation will install a different keymap that resolves to the default keymap for those bindings not found in the different keymap. The minimal bindings include:
- inserting content into the editor for the printable keys.
- removing content with the backspace and del keys.
- caret movement forward and backward
- Model/View Split
-
The text components have a model-view split. A text component pulls
together the objects used to represent the model, view, and controller.
The text document model may be shared by other views which act as observers
of the model (e.g. a document may be shared by multiple components).
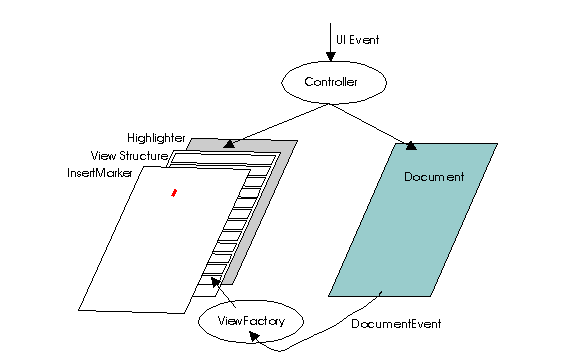
The model is defined by the
Documentinterface. This is intended to provide a flexible text storage mechanism that tracks change during edits and can be extended to more sophisticated models. The model interfaces are meant to capture the capabilities of expression given by SGML, a system used to express a wide variety of content. Each modification to the document causes notification of the details of the change to be sent to all observers in the form of aDocumentEventwhich allows the views to stay up to date with the model. This event is sent to observers that have implemented theDocumentListenerinterface and registered interest with the model being observed. - Location Information
-
The capability of determining the location of text in
the view is provided. There are two methods,
modelToView(int)andviewToModel(Point)for determining this information. - Undo/Redo support
-
Support for an edit history mechanism is provided to allow
undo/redo operations. The text component does not itself
provide the history buffer by default, but does provide
the
UndoableEditrecords that can be used in conjunction with a history buffer to provide the undo/redo support. The support is provided by the Document model, which allows one to attach UndoableEditListener implementations. - Thread Safety
-
The swing text components provide some support of thread
safe operations. Because of the high level of configurability
of the text components, it is possible to circumvent the
protection provided. The protection primarily comes from
the model, so the documentation of
AbstractDocumentdescribes the assumptions of the protection provided. The methods that are safe to call asynchronously are marked with comments. - Newlines
- For a discussion on how newlines are handled, see DefaultEditorKit.
- Printing support
-
Several
printmethods are provided for basic document printing. If more advanced printing is needed, use thegetPrintable(MessageFormat, MessageFormat)method.
Warning:
Serialized objects of this class will not be compatible with
future Swing releases. The current serialization support is
appropriate for short term storage or RMI between applications running
the same version of Swing. As of 1.4, support for long term storage
of all JavaBeans
has been added to the java.beans package.
Please see XMLEncoder.
- See Also:
-
Nested Class Summary
Nested ClassesModifier and TypeClassDescriptionclassThis class implements accessibility support for theJTextComponentclass.static final classRepresents a drop location forJTextComponents.static classBinding record for creating key bindings.Nested classes/interfaces declared in class JComponent
JComponent.AccessibleJComponentNested classes/interfaces declared in class Container
Container.AccessibleAWTContainerNested classes/interfaces declared in class Component
Component.AccessibleAWTComponent, Component.BaselineResizeBehavior, Component.BltBufferStrategy, Component.FlipBufferStrategy -
Field Summary
FieldsModifier and TypeFieldDescriptionstatic final StringThe default keymap that will be shared by allJTextComponentinstances unless they have had a different keymap set.static final StringThe bound property name for the focus accelerator.Fields declared in class JComponent
listenerList, TOOL_TIP_TEXT_KEY, ui, UNDEFINED_CONDITION, WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT, WHEN_FOCUSED, WHEN_IN_FOCUSED_WINDOWFields declared in class Component
accessibleContext, BOTTOM_ALIGNMENT, CENTER_ALIGNMENT, LEFT_ALIGNMENT, RIGHT_ALIGNMENT, TOP_ALIGNMENTFields declared in interface ImageObserver
ABORT, ALLBITS, ERROR, FRAMEBITS, HEIGHT, PROPERTIES, SOMEBITS, WIDTH -
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionvoidaddCaretListener(CaretListener listener) Adds a caret listener for notification of any changes to the caret.static KeymapAdds a new keymap into the keymap hierarchy.voidcopy()Transfers the currently selected range in the associated text model to the system clipboard, leaving the contents in the text model.voidcut()Transfers the currently selected range in the associated text model to the system clipboard, removing the contents from the model.protected voidNotifies all listeners that have registered interest for notification on this event type.Gets theAccessibleContextassociated with thisJTextComponent.Action[]Fetches the command list for the editor.getCaret()Fetches the caret that allows text-oriented navigation over the view.Fetches the current color used to render the caret.Returns an array of all the caret listeners registered on this text component.intReturns the position of the text insertion caret for the text component.Fetches the current color used to render the disabled text.Fetches the model associated with the editor.booleanReturns whether or not automatic drag handling is enabled.Returns the location that this component should visually indicate as the drop location during a DnD operation over the component, ornullif no location is to currently be shown.final DropModeReturns the drop mode for this component.charReturns the key accelerator that will cause the receiving text component to get the focus.Fetches the object responsible for making highlights.Gets the input method request handler which supports requests from input methods for this component.Fetches the keymap currently active in this text component.static KeymapFetches a named keymap previously added to the document.Returns the margin between the text component's border and its text.Returns theNavigationFilter.Returns the preferred size of the viewport for a view component.getPrintable(MessageFormat headerFormat, MessageFormat footerFormat) Returns aPrintableto use for printing the content of thisJTextComponent.intgetScrollableBlockIncrement(Rectangle visibleRect, int orientation, int direction) Components that display logical rows or columns should compute the scroll increment that will completely expose one block of rows or columns, depending on the value of orientation.booleanReturns true if a viewport should always force the height of thisScrollableto match the height of the viewport.booleanReturns true if a viewport should always force the width of thisScrollableto match the width of the viewport.intgetScrollableUnitIncrement(Rectangle visibleRect, int orientation, int direction) Components that display logical rows or columns should compute the scroll increment that will completely expose one new row or column, depending on the value of orientation.Returns the selected text contained in thisTextComponent.Fetches the current color used to render the selected text.Fetches the current color used to render the selection.intReturns the selected text's end position.intReturns the selected text's start position.getText()Returns the text contained in thisTextComponent.getText(int offs, int len) Fetches a portion of the text represented by the component.getToolTipText(MouseEvent event) Returns the string to be used as the tooltip forevent.getUI()Fetches the user-interface factory for this text-oriented editor.booleanReturns the boolean indicating whether thisTextComponentis editable or not.static voidloadKeymap(Keymap map, JTextComponent.KeyBinding[] bindings, Action[] actions) Loads a keymap with a bunch of bindings.modelToView(int pos) Deprecated.modelToView2D(int pos) Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system.voidmoveCaretPosition(int pos) Moves the caret to a new position, leaving behind a mark defined by the last timesetCaretPositionwas called.protected StringReturns a string representation of thisJTextComponent.voidpaste()Transfers the contents of the system clipboard into the associated text model.booleanprint()A convenience print method that displays a print dialog, and then prints thisJTextComponentin interactive mode with no header or footer text.booleanprint(MessageFormat headerFormat, MessageFormat footerFormat) A convenience print method that displays a print dialog, and then prints thisJTextComponentin interactive mode with the specified header and footer text.booleanprint(MessageFormat headerFormat, MessageFormat footerFormat, boolean showPrintDialog, PrintService service, PrintRequestAttributeSet attributes, boolean interactive) Prints the content of thisJTextComponent.voidInitializes from a stream.voidremoveCaretListener(CaretListener listener) Removes a caret listener.static KeymapremoveKeymap(String nm) Removes a named keymap previously added to the document.voidreplaceSelection(String content) Replaces the currently selected content with new content represented by the given string.protected voidRestores composed text previously saved bysaveComposedText.protected booleansaveComposedText(int pos) Saves composed text around the specified position.voidselect(int selectionStart, int selectionEnd) Selects the text between the specified start and end positions.voidSelects all the text in theTextComponent.voidSets the caret to be used.voidSets the current color used to render the caret.voidsetCaretPosition(int position) Sets the position of the text insertion caret for theTextComponent.voidSets the current color used to render the disabled text.voidsetDocument(Document doc) Associates the editor with a text document.voidsetDragEnabled(boolean b) Turns on or off automatic drag handling.final voidsetDropMode(DropMode dropMode) Sets the drop mode for this component.voidsetEditable(boolean b) Sets the specified boolean to indicate whether or not thisTextComponentshould be editable.voidsetFocusAccelerator(char aKey) Sets the key accelerator that will cause the receiving text component to get the focus.voidSets the highlighter to be used.voidSets the keymap to use for binding events to actions.voidSets margin space between the text component's border and its text.voidsetNavigationFilter(NavigationFilter filter) Sets theNavigationFilter.voidSets the current color used to render the selected text.voidSets the current color used to render the selection.voidsetSelectionEnd(int selectionEnd) Sets the selection end to the specified position.voidsetSelectionStart(int selectionStart) Sets the selection start to the specified position.voidSets the text of thisTextComponentto the specified text.voidSets the user-interface factory for this text-oriented editor.voidupdateUI()Reloads the pluggable UI.intviewToModel(Point pt) Deprecated.replaced byviewToModel2D(Point2D)intviewToModel2D(Point2D pt) Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model.voidStores the contents of the model into the given stream.Methods declared in class JComponent
addAncestorListener, addNotify, addVetoableChangeListener, computeVisibleRect, contains, createToolTip, disable, enable, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, fireVetoableChange, getActionForKeyStroke, getActionMap, getAlignmentX, getAlignmentY, getAncestorListeners, getAutoscrolls, getBaseline, getBaselineResizeBehavior, getBorder, getBounds, getClientProperty, getComponentGraphics, getComponentPopupMenu, getConditionForKeyStroke, getDebugGraphicsOptions, getDefaultLocale, getFontMetrics, getGraphics, getHeight, getInheritsPopupMenu, getInputMap, getInputMap, getInputVerifier, getInsets, getInsets, getListeners, getLocation, getMaximumSize, getMinimumSize, getNextFocusableComponent, getPopupLocation, getPreferredSize, getRegisteredKeyStrokes, getRootPane, getSize, getToolTipLocation, getToolTipText, getTopLevelAncestor, getTransferHandler, getUIClassID, getVerifyInputWhenFocusTarget, getVetoableChangeListeners, getVisibleRect, getWidth, getX, getY, grabFocus, hide, isDoubleBuffered, isLightweightComponent, isManagingFocus, isOpaque, isOptimizedDrawingEnabled, isPaintingForPrint, isPaintingOrigin, isPaintingTile, isRequestFocusEnabled, isValidateRoot, paint, paintBorder, paintChildren, paintComponent, paintImmediately, paintImmediately, print, printAll, printBorder, printChildren, printComponent, processComponentKeyEvent, processKeyBinding, processKeyEvent, processMouseEvent, processMouseMotionEvent, putClientProperty, registerKeyboardAction, registerKeyboardAction, removeAncestorListener, removeNotify, removeVetoableChangeListener, repaint, repaint, requestDefaultFocus, requestFocus, requestFocus, requestFocusInWindow, requestFocusInWindow, resetKeyboardActions, reshape, revalidate, scrollRectToVisible, setActionMap, setAlignmentX, setAlignmentY, setAutoscrolls, setBackground, setBorder, setComponentPopupMenu, setDebugGraphicsOptions, setDefaultLocale, setDoubleBuffered, setEnabled, setFocusTraversalKeys, setFont, setForeground, setInheritsPopupMenu, setInputMap, setInputVerifier, setMaximumSize, setMinimumSize, setNextFocusableComponent, setOpaque, setPreferredSize, setRequestFocusEnabled, setToolTipText, setTransferHandler, setUI, setVerifyInputWhenFocusTarget, setVisible, unregisterKeyboardAction, updateMethods declared in class Container
add, add, add, add, add, addContainerListener, addImpl, addPropertyChangeListener, addPropertyChangeListener, applyComponentOrientation, areFocusTraversalKeysSet, countComponents, deliverEvent, doLayout, findComponentAt, findComponentAt, getComponent, getComponentAt, getComponentAt, getComponentCount, getComponents, getComponentZOrder, getContainerListeners, getFocusTraversalKeys, getFocusTraversalPolicy, getLayout, getMousePosition, insets, invalidate, isAncestorOf, isFocusCycleRoot, isFocusCycleRoot, isFocusTraversalPolicyProvider, isFocusTraversalPolicySet, layout, list, list, locate, minimumSize, paintComponents, preferredSize, printComponents, processContainerEvent, processEvent, remove, remove, removeAll, removeContainerListener, setComponentZOrder, setFocusCycleRoot, setFocusTraversalPolicy, setFocusTraversalPolicyProvider, setLayout, transferFocusDownCycle, validate, validateTreeMethods declared in class Component
action, add, addComponentListener, addFocusListener, addHierarchyBoundsListener, addHierarchyListener, addInputMethodListener, addKeyListener, addMouseListener, addMouseMotionListener, addMouseWheelListener, bounds, checkImage, checkImage, coalesceEvents, contains, createImage, createImage, createVolatileImage, createVolatileImage, disableEvents, dispatchEvent, enable, enableEvents, enableInputMethods, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, firePropertyChange, getBackground, getBounds, getColorModel, getComponentListeners, getComponentOrientation, getCursor, getDropTarget, getFocusCycleRootAncestor, getFocusListeners, getFocusTraversalKeysEnabled, getFont, getForeground, getGraphicsConfiguration, getHierarchyBoundsListeners, getHierarchyListeners, getIgnoreRepaint, getInputContext, getInputMethodListeners, getKeyListeners, getLocale, getLocation, getLocationOnScreen, getMouseListeners, getMouseMotionListeners, getMousePosition, getMouseWheelListeners, getName, getParent, getPropertyChangeListeners, getPropertyChangeListeners, getSize, getToolkit, getTreeLock, gotFocus, handleEvent, hasFocus, imageUpdate, inside, isBackgroundSet, isCursorSet, isDisplayable, isEnabled, isFocusable, isFocusOwner, isFocusTraversable, isFontSet, isForegroundSet, isLightweight, isMaximumSizeSet, isMinimumSizeSet, isPreferredSizeSet, isShowing, isValid, isVisible, keyDown, keyUp, list, list, list, location, lostFocus, mouseDown, mouseDrag, mouseEnter, mouseExit, mouseMove, mouseUp, move, nextFocus, paintAll, postEvent, prepareImage, prepareImage, processComponentEvent, processFocusEvent, processHierarchyBoundsEvent, processHierarchyEvent, processInputMethodEvent, processMouseWheelEvent, remove, removeComponentListener, removeFocusListener, removeHierarchyBoundsListener, removeHierarchyListener, removeInputMethodListener, removeKeyListener, removeMouseListener, removeMouseMotionListener, removeMouseWheelListener, removePropertyChangeListener, removePropertyChangeListener, repaint, repaint, repaint, requestFocus, requestFocus, requestFocusInWindow, resize, resize, setBounds, setBounds, setComponentOrientation, setCursor, setDropTarget, setFocusable, setFocusTraversalKeysEnabled, setIgnoreRepaint, setLocale, setLocation, setLocation, setMixingCutoutShape, setName, setSize, setSize, show, show, size, toString, transferFocus, transferFocusBackward, transferFocusUpCycle
-
Field Details
-
FOCUS_ACCELERATOR_KEY
The bound property name for the focus accelerator.- See Also:
-
DEFAULT_KEYMAP
The default keymap that will be shared by allJTextComponentinstances unless they have had a different keymap set.- See Also:
-
-
Constructor Details
-
JTextComponent
public JTextComponent()Creates a newJTextComponent. Listeners for caret events are established, and the pluggable UI installed. The component is marked as editable. No layout manager is used, because layout is managed by the view subsystem of text. The document model is set tonull.
-
-
Method Details
-
getUI
Fetches the user-interface factory for this text-oriented editor.- Overrides:
getUIin classJComponent- Returns:
- the factory
-
setUI
Sets the user-interface factory for this text-oriented editor.- Parameters:
ui- the factory
-
updateUI
public void updateUI()Reloads the pluggable UI. The key used to fetch the new interface isgetUIClassID(). The type of the UI isTextUI.invalidateis called after setting the UI.- Overrides:
updateUIin classJComponent- See Also:
-
addCaretListener
Adds a caret listener for notification of any changes to the caret.- Parameters:
listener- the listener to be added- See Also:
-
removeCaretListener
Removes a caret listener.- Parameters:
listener- the listener to be removed- See Also:
-
getCaretListeners
Returns an array of all the caret listeners registered on this text component.- Returns:
- all of this component's
CaretListeners or an empty array if no caret listeners are currently registered - Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
-
fireCaretUpdate
Notifies all listeners that have registered interest for notification on this event type. The event instance is lazily created using the parameters passed into the fire method. The listener list is processed in a last-to-first manner.- Parameters:
e- the event- See Also:
-
setDocument
@BeanProperty(expert=true, description="the text document model") public void setDocument(Document doc) Associates the editor with a text document. The currently registered factory is used to build a view for the document, which gets displayed by the editor after revalidation. A PropertyChange event ("document") is propagated to each listener.- Parameters:
doc- the document to display/edit- See Also:
-
getDocument
Fetches the model associated with the editor. This is primarily for the UI to get at the minimal amount of state required to be a text editor. Subclasses will return the actual type of the model which will typically be something that extends Document.- Returns:
- the model
-
getActions
Fetches the command list for the editor. This is the list of commands supported by the plugged-in UI augmented by the collection of commands that the editor itself supports. These are useful for binding to events, such as in a keymap.- Returns:
- the command list
-
setMargin
@BeanProperty(description="desired space between the border and text area") public void setMargin(Insets m) Sets margin space between the text component's border and its text. The text component's defaultBorderobject will use this value to create the proper margin. However, if a non-default border is set on the text component, it is thatBorderobject's responsibility to create the appropriate margin space (else this property will effectively be ignored). This causes a redraw of the component. A PropertyChange event ("margin") is sent to all listeners.- Parameters:
m- the space between the border and the text
-
getMargin
Returns the margin between the text component's border and its text.- Returns:
- the margin
-
getCaret
Fetches the caret that allows text-oriented navigation over the view.- Returns:
- the caret
-
setCaret
@BeanProperty(expert=true, description="the caret used to select/navigate") public void setCaret(Caret c) Sets the caret to be used. By default this will be set by the UI that gets installed. This can be changed to a custom caret if desired. Setting the caret results in a PropertyChange event ("caret") being fired.- Parameters:
c- the caret- See Also:
-
getHighlighter
Fetches the object responsible for making highlights.- Returns:
- the highlighter
-
setHighlighter
@BeanProperty(expert=true, description="object responsible for background highlights") public void setHighlighter(Highlighter h) Sets the highlighter to be used. By default this will be set by the UI that gets installed. This can be changed to a custom highlighter if desired. The highlighter can be set tonullto disable it. A PropertyChange event ("highlighter") is fired when a new highlighter is installed.- Parameters:
h- the highlighter- See Also:
-
setKeymap
@BeanProperty(description="set of key event to action bindings to use") public void setKeymap(Keymap map) Sets the keymap to use for binding events to actions. Setting tonulleffectively disables keyboard input. A PropertyChange event ("keymap") is fired when a new keymap is installed.- Parameters:
map- the keymap- See Also:
-
setDragEnabled
@BeanProperty(bound=false, description="determines whether automatic drag handling is enabled") public void setDragEnabled(boolean b) Turns on or off automatic drag handling. In order to enable automatic drag handling, this property should be set totrue, and the component'sTransferHandlerneeds to benon-null. The default value of thedragEnabledproperty isfalse.The job of honoring this property, and recognizing a user drag gesture, lies with the look and feel implementation, and in particular, the component's
TextUI. When automatic drag handling is enabled, most look and feels (including those that subclassBasicLookAndFeel) begin a drag and drop operation whenever the user presses the mouse button over a selection and then moves the mouse a few pixels. Setting this property totruecan therefore have a subtle effect on how selections behave.If a look and feel is used that ignores this property, you can still begin a drag and drop operation by calling
exportAsDragon the component'sTransferHandler.- Parameters:
b- whether or not to enable automatic drag handling- Throws:
HeadlessException- ifbistrueandGraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()returnstrue- Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
-
getDragEnabled
public boolean getDragEnabled()Returns whether or not automatic drag handling is enabled.- Returns:
- the value of the
dragEnabledproperty - Since:
- 1.4
- See Also:
-
setDropMode
Sets the drop mode for this component. For backward compatibility, the default for this property isDropMode.USE_SELECTION. Usage ofDropMode.INSERTis recommended, however, for an improved user experience. It offers similar behavior of dropping between text locations, but does so without affecting the actual text selection and caret location.JTextComponentssupport the following drop modes:DropMode.USE_SELECTIONDropMode.INSERT
The drop mode is only meaningful if this component has a
TransferHandlerthat accepts drops.- Parameters:
dropMode- the drop mode to use- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the drop mode is unsupported ornull- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
getDropMode
Returns the drop mode for this component.- Returns:
- the drop mode for this component
- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
getDropLocation
Returns the location that this component should visually indicate as the drop location during a DnD operation over the component, ornullif no location is to currently be shown.This method is not meant for querying the drop location from a
TransferHandler, as the drop location is only set after theTransferHandler'scanImporthas returned and has allowed for the location to be shown.When this property changes, a property change event with name "dropLocation" is fired by the component.
- Returns:
- the drop location
- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
getKeymap
Fetches the keymap currently active in this text component.- Returns:
- the keymap
-
addKeymap
Adds a new keymap into the keymap hierarchy. Keymap bindings resolve from bottom up so an attribute specified in a child will override an attribute specified in the parent.- Parameters:
nm- the name of the keymap (must be unique within the collection of named keymaps in the document); the name may benullif the keymap is unnamed, but the caller is responsible for managing the reference returned as an unnamed keymap can't be fetched by nameparent- the parent keymap; this may benullif unspecified bindings need not be resolved in some other keymap- Returns:
- the keymap
-
removeKeymap
-
getKeymap
-
loadKeymap
Loads a keymap with a bunch of bindings. This can be used to take a static table of definitions and load them into some keymap. The following example illustrates an example of binding some keys to the cut, copy, and paste actions associated with a JTextComponent. A code fragment to accomplish this might look as follows:
The sets of bindings and actions may be empty but must be non-static final JTextComponent.KeyBinding[] defaultBindings = { new JTextComponent.KeyBinding( KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_C, InputEvent.CTRL_MASK), DefaultEditorKit.copyAction), new JTextComponent.KeyBinding( KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_V, InputEvent.CTRL_MASK), DefaultEditorKit.pasteAction), new JTextComponent.KeyBinding( KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_X, InputEvent.CTRL_MASK), DefaultEditorKit.cutAction), }; JTextComponent c = new JTextPane(); Keymap k = c.getKeymap(); JTextComponent.loadKeymap(k, defaultBindings, c.getActions());null.- Parameters:
map- the keymapbindings- the bindingsactions- the set of actions
-
getCaretColor
-
setCaretColor
@BeanProperty(preferred=true, description="the color used to render the caret") public void setCaretColor(Color c) Sets the current color used to render the caret. Setting tonulleffectively restores the default color. Setting the color results in a PropertyChange event ("caretColor") being fired.- Parameters:
c- the color- See Also:
-
getSelectionColor
Fetches the current color used to render the selection.- Returns:
- the color
-
setSelectionColor
@BeanProperty(preferred=true, description="color used to render selection background") public void setSelectionColor(Color c) Sets the current color used to render the selection. Setting the color tonullis the same as settingColor.white. Setting the color results in a PropertyChange event ("selectionColor").- Parameters:
c- the color- See Also:
-
getSelectedTextColor
Fetches the current color used to render the selected text.- Returns:
- the color
-
setSelectedTextColor
@BeanProperty(preferred=true, description="color used to render selected text") public void setSelectedTextColor(Color c) Sets the current color used to render the selected text. Setting the color tonullis the same asColor.black. Setting the color results in a PropertyChange event ("selectedTextColor") being fired.- Parameters:
c- the color- See Also:
-
getDisabledTextColor
Fetches the current color used to render the disabled text.- Returns:
- the color
-
setDisabledTextColor
@BeanProperty(preferred=true, description="color used to render disabled text") public void setDisabledTextColor(Color c) Sets the current color used to render the disabled text. Setting the color fires off a PropertyChange event ("disabledTextColor").- Parameters:
c- the color- See Also:
-
replaceSelection
Replaces the currently selected content with new content represented by the given string. If there is no selection this amounts to an insert of the given text. If there is no replacement text this amounts to a removal of the current selection.This is the method that is used by the default implementation of the action for inserting content that gets bound to the keymap actions.
- Parameters:
content- the content to replace the selection with
-
getText
Fetches a portion of the text represented by the component. Returns an empty string if length is 0.- Parameters:
offs- the offset ≥ 0len- the length ≥ 0- Returns:
- the text
- Throws:
BadLocationException- if the offset or length are invalid
-
modelToView
Deprecated.replaced bymodelToView2D(int)Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. The component must have a positive size for this translation to be computed (i.e. layout cannot be computed until the component has been sized). The component does not have to be visible or painted.- Parameters:
pos- the position ≥ 0- Returns:
- the coordinates as a rectangle, with (r.x, r.y) as the location in the coordinate system, or null if the component does not yet have a positive size.
- Throws:
BadLocationException- if the given position does not represent a valid location in the associated document- See Also:
-
modelToView2D
Converts the given location in the model to a place in the view coordinate system. The component must have a positive size for this translation to be computed (i.e. layout cannot be computed until the component has been sized). The component does not have to be visible or painted.- Parameters:
pos- the position>= 0- Returns:
- the coordinates as a rectangle, with (r.x, r.y) as the location in the coordinate system, or null if the component does not yet have a positive size.
- Throws:
BadLocationException- if the given position does not represent a valid location in the associated document- Since:
- 9
- See Also:
-
viewToModel
Deprecated.replaced byviewToModel2D(Point2D)Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. The component must have a positive size for this translation to be computed (i.e. layout cannot be computed until the component has been sized). The component does not have to be visible or painted.- Parameters:
pt- the location in the view to translate- Returns:
- the offset ≥ 0 from the start of the document, or -1 if the component does not yet have a positive size.
- See Also:
-
viewToModel2D
Converts the given place in the view coordinate system to the nearest representative location in the model. The component must have a positive size for this translation to be computed (i.e. layout cannot be computed until the component has been sized). The component does not have to be visible or painted.- Parameters:
pt- the location in the view to translate- Returns:
- the offset
>= 0from the start of the document, or-1if the component does not yet have a positive size. - Since:
- 9
- See Also:
-
cut
public void cut()Transfers the currently selected range in the associated text model to the system clipboard, removing the contents from the model. The current selection is reset. Does nothing fornullselections.- See Also:
-
copy
public void copy()Transfers the currently selected range in the associated text model to the system clipboard, leaving the contents in the text model. The current selection remains intact. Does nothing fornullselections.- See Also:
-
paste
public void paste()Transfers the contents of the system clipboard into the associated text model. If there is a selection in the associated view, it is replaced with the contents of the clipboard. If there is no selection, the clipboard contents are inserted in front of the current insert position in the associated view. If the clipboard is empty, does nothing.- See Also:
-
moveCaretPosition
public void moveCaretPosition(int pos) Moves the caret to a new position, leaving behind a mark defined by the last timesetCaretPositionwas called. This forms a selection. If the document isnull, does nothing. The position must be between 0 and the length of the component's text or else an exception is thrown.- Parameters:
pos- the position- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the value supplied forpositionis less than zero or greater than the component's text length- See Also:
-
setFocusAccelerator
@BeanProperty(description="accelerator character used to grab focus") public void setFocusAccelerator(char aKey) Sets the key accelerator that will cause the receiving text component to get the focus. The accelerator will be the key combination of the platform-specific modifier key and the character given (converted to upper case). For example, the ALT key is used as a modifier on Windows and the CTRL+ALT combination is used on Mac. By default, there is no focus accelerator key. Any previous key accelerator setting will be superseded. A '\0' key setting will be registered, and has the effect of turning off the focus accelerator. When the new key is set, a PropertyChange event (FOCUS_ACCELERATOR_KEY) will be fired.- Parameters:
aKey- the key- See Also:
-
getFocusAccelerator
public char getFocusAccelerator()Returns the key accelerator that will cause the receiving text component to get the focus. Return '\0' if no focus accelerator has been set.- Returns:
- the key
-
read
Initializes from a stream. This creates a model of the type appropriate for the component and initializes the model from the stream. By default this will load the model as plain text. Previous contents of the model are discarded.- Parameters:
in- the stream to read fromdesc- an object describing the stream; this might be a string, a File, a URL, etc. Some kinds of documents (such as html for example) might be able to make use of this information; if non-null, it is added as a property of the document- Throws:
IOException- as thrown by the stream being used to initialize- See Also:
-
write
Stores the contents of the model into the given stream. By default this will store the model as plain text.- Parameters:
out- the output stream- Throws:
IOException- on any I/O error
-
setCaretPosition
@BeanProperty(bound=false, description="the caret position") public void setCaretPosition(int position) Sets the position of the text insertion caret for theTextComponent. Note that the caret tracks change, so this may move if the underlying text of the component is changed. If the document isnull, does nothing. The position must be between 0 and the length of the component's text or else an exception is thrown.- Parameters:
position- the position- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the value supplied forpositionis less than zero or greater than the component's text length
-
getCaretPosition
public int getCaretPosition()Returns the position of the text insertion caret for the text component.- Returns:
- the position of the text insertion caret for the text component ≥ 0
-
setText
Sets the text of thisTextComponentto the specified text. If the text isnullor empty, has the effect of simply deleting the old text. When text has been inserted, the resulting caret location is determined by the implementation of the caret class.Note that text is not a bound property, so no
PropertyChangeEventis fired when it changes. To listen for changes to the text, useDocumentListener.- Parameters:
t- the new text to be set- See Also:
-
getText
Returns the text contained in thisTextComponent. If the underlying document isnull, will give aNullPointerException. Note that text is not a bound property, so noPropertyChangeEventis fired when it changes. To listen for changes to the text, useDocumentListener.- Returns:
- the text
- Throws:
NullPointerException- if the document isnull- See Also:
-
getSelectedText
Returns the selected text contained in thisTextComponent. If the selection isnullor the document empty, returnsnull.- Returns:
- the text
- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the selection doesn't have a valid mapping into the document for some reason- See Also:
-
isEditable
public boolean isEditable()Returns the boolean indicating whether thisTextComponentis editable or not.- Returns:
- the boolean value
- See Also:
-
setEditable
Sets the specified boolean to indicate whether or not thisTextComponentshould be editable. A PropertyChange event ("editable") is fired when the state is changed.- Parameters:
b- the boolean to be set- See Also:
-
getSelectionStart
public int getSelectionStart()Returns the selected text's start position. Return 0 for an empty document, or the value of dot if no selection.- Returns:
- the start position ≥ 0
-
setSelectionStart
@BeanProperty(bound=false, description="starting location of the selection.") public void setSelectionStart(int selectionStart) Sets the selection start to the specified position. The new starting point is constrained to be before or at the current selection end.This is available for backward compatibility to code that called this method on
java.awt.TextComponent. This is implemented to forward to theCaretimplementation which is where the actual selection is maintained.- Parameters:
selectionStart- the start position of the text ≥ 0
-
getSelectionEnd
public int getSelectionEnd()Returns the selected text's end position. Return 0 if the document is empty, or the value of dot if there is no selection.- Returns:
- the end position ≥ 0
-
setSelectionEnd
@BeanProperty(bound=false, description="ending location of the selection.") public void setSelectionEnd(int selectionEnd) Sets the selection end to the specified position. The new end point is constrained to be at or after the current selection start.This is available for backward compatibility to code that called this method on
java.awt.TextComponent. This is implemented to forward to theCaretimplementation which is where the actual selection is maintained.- Parameters:
selectionEnd- the end position of the text ≥ 0
-
select
public void select(int selectionStart, int selectionEnd) Selects the text between the specified start and end positions.This method sets the start and end positions of the selected text, enforcing the restriction that the start position must be greater than or equal to zero. The end position must be greater than or equal to the start position, and less than or equal to the length of the text component's text.
If the caller supplies values that are inconsistent or out of bounds, the method enforces these constraints silently, and without failure. Specifically, if the start position or end position is greater than the length of the text, it is reset to equal the text length. If the start position is less than zero, it is reset to zero, and if the end position is less than the start position, it is reset to the start position.
This call is provided for backward compatibility. It is routed to a call to
setCaretPositionfollowed by a call tomoveCaretPosition. The preferred way to manage selection is by calling those methods directly.- Parameters:
selectionStart- the start position of the textselectionEnd- the end position of the text- See Also:
-
selectAll
public void selectAll()Selects all the text in theTextComponent. Does nothing on anullor empty document. -
getToolTipText
Returns the string to be used as the tooltip forevent. This will return one of:- If
setToolTipTexthas been invoked with a non-nullvalue, it will be returned, otherwise - The value from invoking
getToolTipTexton the UI will be returned.
JTextComponentdoes not register itself with theToolTipManager. This means that tooltips will NOT be shown from theTextUIunlessregisterComponenthas been invoked on theToolTipManager.- Overrides:
getToolTipTextin classJComponent- Parameters:
event- the event in question- Returns:
- the string to be used as the tooltip for
event - See Also:
- If
-
getPreferredScrollableViewportSize
Returns the preferred size of the viewport for a view component. This is implemented to do the default behavior of returning the preferred size of the component.- Specified by:
getPreferredScrollableViewportSizein interfaceScrollable- Returns:
- the
preferredSizeof aJViewportwhose view is thisScrollable - See Also:
-
getScrollableUnitIncrement
Components that display logical rows or columns should compute the scroll increment that will completely expose one new row or column, depending on the value of orientation. Ideally, components should handle a partially exposed row or column by returning the distance required to completely expose the item.The default implementation of this is to simply return 10% of the visible area. Subclasses are likely to be able to provide a much more reasonable value.
- Specified by:
getScrollableUnitIncrementin interfaceScrollable- Parameters:
visibleRect- the view area visible within the viewportorientation- eitherSwingConstants.VERTICALorSwingConstants.HORIZONTALdirection- less than zero to scroll up/left, greater than zero for down/right- Returns:
- the "unit" increment for scrolling in the specified direction
- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- for an invalid orientation- See Also:
-
getScrollableBlockIncrement
Components that display logical rows or columns should compute the scroll increment that will completely expose one block of rows or columns, depending on the value of orientation.The default implementation of this is to simply return the visible area. Subclasses will likely be able to provide a much more reasonable value.
- Specified by:
getScrollableBlockIncrementin interfaceScrollable- Parameters:
visibleRect- the view area visible within the viewportorientation- eitherSwingConstants.VERTICALorSwingConstants.HORIZONTALdirection- less than zero to scroll up/left, greater than zero for down/right- Returns:
- the "block" increment for scrolling in the specified direction
- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- for an invalid orientation- See Also:
-
getScrollableTracksViewportWidth
Returns true if a viewport should always force the width of thisScrollableto match the width of the viewport. For example a normal text view that supported line wrapping would return true here, since it would be undesirable for wrapped lines to disappear beyond the right edge of the viewport. Note that returning true for aScrollablewhose ancestor is aJScrollPaneeffectively disables horizontal scrolling.Scrolling containers, like
JViewport, will use this method each time they are validated.- Specified by:
getScrollableTracksViewportWidthin interfaceScrollable- Returns:
- true if a viewport should force the
Scrollables width to match its own
-
getScrollableTracksViewportHeight
Returns true if a viewport should always force the height of thisScrollableto match the height of the viewport. For example a columnar text view that flowed text in left to right columns could effectively disable vertical scrolling by returning true here.Scrolling containers, like
JViewport, will use this method each time they are validated.- Specified by:
getScrollableTracksViewportHeightin interfaceScrollable- Returns:
- true if a viewport should force the Scrollables height to match its own
-
print
A convenience print method that displays a print dialog, and then prints thisJTextComponentin interactive mode with no header or footer text. Note: this method blocks until printing is done.Note: In headless mode, no dialogs will be shown.
This method calls the full featured
printmethod to perform printing.- Returns:
true, unless printing is canceled by the user- Throws:
PrinterException- if an error in the print system causes the job to be aborted- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
print
public boolean print(MessageFormat headerFormat, MessageFormat footerFormat) throws PrinterException A convenience print method that displays a print dialog, and then prints thisJTextComponentin interactive mode with the specified header and footer text. Note: this method blocks until printing is done.Note: In headless mode, no dialogs will be shown.
This method calls the full featured
printmethod to perform printing.- Parameters:
headerFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the header, ornullfor no headerfooterFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the footer, ornullfor no footer- Returns:
true, unless printing is canceled by the user- Throws:
PrinterException- if an error in the print system causes the job to be aborted- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
print
public boolean print(MessageFormat headerFormat, MessageFormat footerFormat, boolean showPrintDialog, PrintService service, PrintRequestAttributeSet attributes, boolean interactive) throws PrinterException Prints the content of thisJTextComponent. Note: this method blocks until printing is done.Page header and footer text can be added to the output by providing
MessageFormatarguments. The printing code requestsStringsfrom the formats, providing a single item which may be included in the formatted string: anIntegerrepresenting the current page number.showPrintDialog booleanparameter allows you to specify whether a print dialog is displayed to the user. When it is, the user may use the dialog to change printing attributes or even cancel the print.serviceallows you to provide the initialPrintServicefor the print dialog, or to specifyPrintServiceto print to when the dialog is not shown.attributescan be used to provide the initial values for the print dialog, or to supply any needed attributes when the dialog is not shown.attributescan be used to control how the job will print, for example duplex or single-sided.interactive booleanparameter allows you to specify whether to perform printing in interactive mode. Iftrue, a progress dialog, with an abort option, is displayed for the duration of printing. This dialog is modal whenprintis invoked on the Event Dispatch Thread and non-modal otherwise. Warning: calling this method on the Event Dispatch Thread withinteractive falseblocks all events, including repaints, from being processed until printing is complete. It is only recommended when printing from an application with no visible GUI.Note: In headless mode,
showPrintDialogandinteractiveparameters are ignored and no dialogs are shown.This method ensures the
documentis not mutated during printing. To indicate it visually,setEnabled(false)is set for the duration of printing.This method uses
getPrintable(MessageFormat, MessageFormat)to render document content.This method is thread-safe, although most Swing methods are not. Please see Concurrency in Swing for more information.
Sample Usage. This code snippet shows a cross-platform print dialog and then prints the
JTextComponentin interactive mode unless the user cancels the dialog:textComponent.print(new MessageFormat("My text component header"), new MessageFormat("Footer. Page - {0}"), true, null, null, true);Executing this code off the Event Dispatch Thread performs printing on the background. The following pattern might be used for background printing:
FutureTask<Boolean> future = new FutureTask<Boolean>( new Callable<Boolean>() { public Boolean call() { return textComponent.print(.....); } }); executor.execute(future);- Parameters:
headerFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the header, ornullfor no headerfooterFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the footer, ornullfor no footershowPrintDialog-trueto display a print dialog,falseotherwiseservice- initialPrintService, ornullfor the defaultattributes- the job attributes to be applied to the print job, ornullfor noneinteractive- whether to print in an interactive mode- Returns:
true, unless printing is canceled by the user- Throws:
PrinterException- if an error in the print system causes the job to be aborted- Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
getPrintable
Returns aPrintableto use for printing the content of thisJTextComponent. The returnedPrintableprints the document as it looks on the screen except being reformatted to fit the paper. The returnedPrintablecan be wrapped inside anotherPrintablein order to create complex reports and documents.The returned
Printableshares thedocumentwith thisJTextComponent. It is the responsibility of the developer to ensure that thedocumentis not mutated while thisPrintableis used. Printing behavior is undefined when thedocumentis mutated during printing.Page header and footer text can be added to the output by providing
MessageFormatarguments. The printing code requestsStringsfrom the formats, providing a single item which may be included in the formatted string: anIntegerrepresenting the current page number.The returned
Printablewhen printed, formats the document content appropriately for the page size. For correct line wrapping theimageable widthof all pages must be the same. SeePageFormat.getImageableWidth().This method is thread-safe, although most Swing methods are not. Please see Concurrency in Swing for more information.
The returned
Printablecan be printed on any thread.This implementation returned
Printableperforms all painting on the Event Dispatch Thread, regardless of what thread it is used on.- Parameters:
headerFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the header, ornullfor no headerfooterFormat- the text, inMessageFormat, to be used as the footer, ornullfor no footer- Returns:
- a
Printablefor use in printing content of thisJTextComponent - Since:
- 1.6
- See Also:
-
getAccessibleContext
Gets theAccessibleContextassociated with thisJTextComponent. For text components, theAccessibleContexttakes the form of anAccessibleJTextComponent. A newAccessibleJTextComponentinstance is created if necessary.- Specified by:
getAccessibleContextin interfaceAccessible- Overrides:
getAccessibleContextin classComponent- Returns:
- an
AccessibleJTextComponentthat serves as theAccessibleContextof thisJTextComponent
-
paramString
Returns a string representation of thisJTextComponent. This method is intended to be used only for debugging purposes, and the content and format of the returned string may vary between implementations. The returned string may be empty but may not benull.Overriding
paramStringto provide information about the specific new aspects of the JFC components.- Overrides:
paramStringin classJComponent- Returns:
- a string representation of this
JTextComponent
-
getInputMethodRequests
Description copied from class:ComponentGets the input method request handler which supports requests from input methods for this component. A component that supports on-the-spot text input must override this method to return anInputMethodRequestsinstance. At the same time, it also has to handle input method events.- Overrides:
getInputMethodRequestsin classComponent- Returns:
- the input method request handler for this component,
nullby default - See Also:
-
saveComposedText
protected boolean saveComposedText(int pos) Saves composed text around the specified position. The composed text (if any) around the specified position is saved in a backing store and removed from the document.- Parameters:
pos- document position to identify the composed text location- Returns:
trueif the composed text exists and is saved,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.7
- See Also:
-
restoreComposedText
protected void restoreComposedText()Restores composed text previously saved bysaveComposedText. The saved composed text is inserted back into the document. This method should be invoked only ifsaveComposedTextreturnstrue.- Since:
- 1.7
- See Also:
-
modelToView2D(int)